Have you ever asked a chatbot something simple and received a strange reply?
Many people wonder how AI Agents Talk and Respond to Users in a way that feels natural one moment and confusing the next. The answer lies in how these systems process language, detect intent, and manage context behind the scenes.
Modern AI agents do much more than generate random text. They analyze patterns, predict responses, and adjust tone based on your input. Once you understand the mechanics, the behavior starts to make sense.
How AI Agents Talk and Respond to Users
When someone types a message, the AI agent does not “think” in the human sense. Instead, the system predicts the next likely words based on patterns learned from large datasets.
The process feels instant, but several internal steps happen quickly. The model reads the input, detects intent, checks conversation context, and then generates a response that fits both meaning and tone.
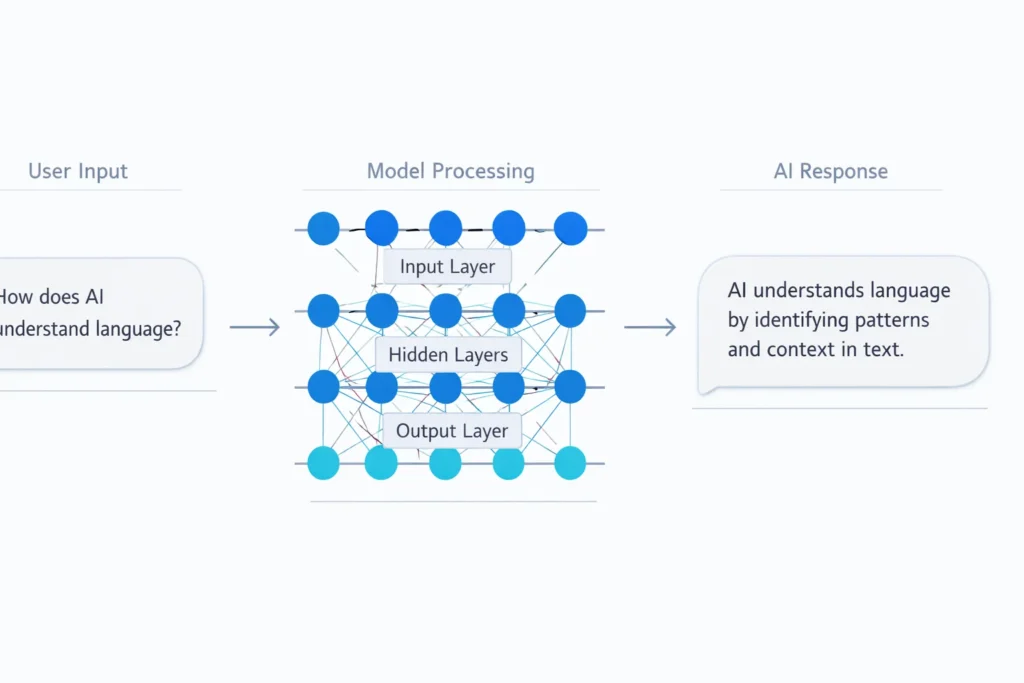
This layered process explains why responses often feel smooth and connected.
Understanding User Intent
Intent detection comes first. If someone writes, “Set an alarm for 6 AM,” the AI recognizes a command. If someone asks, “Why do we need sleep?” the system switches to explanation mode.
Intent helps the AI decide the purpose behind the message. Without this step, replies would miss the point.
Modern AI systems train on large volumes of conversational data. That training helps the system recognize subtle differences between requests, questions, and casual remarks.
How Context Keeps Conversations Natural
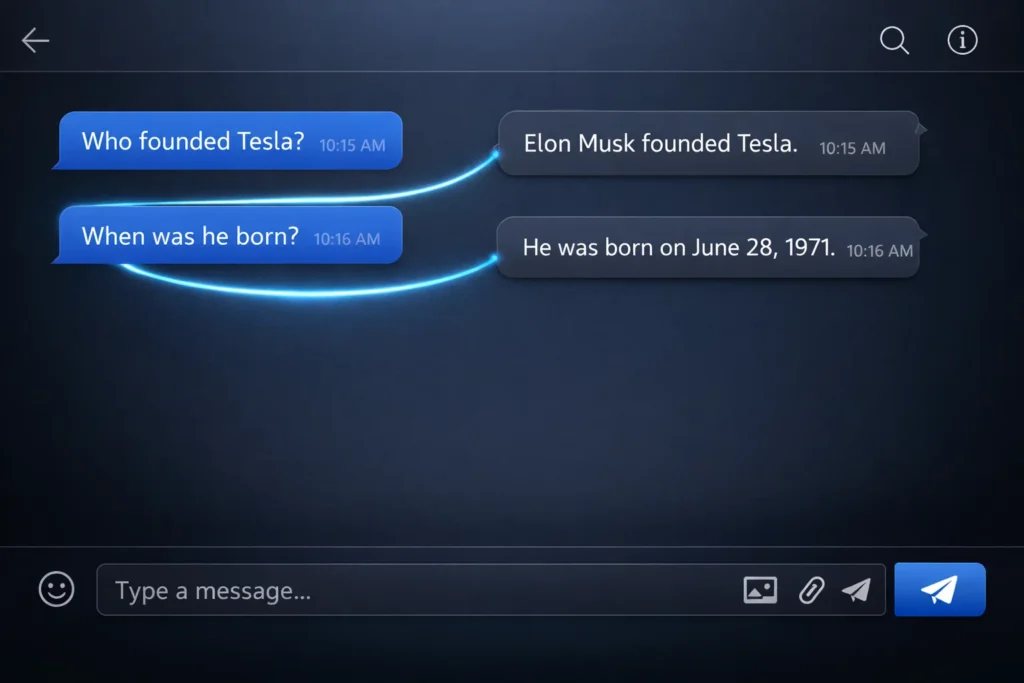
A single message rarely stands alone. Most conversations include follow-up questions.
If you ask, “Who founded Tesla?” and then ask, “When was he born?”, the AI connects the second question to Elon Musk. Context tracking allows that connection.
Without context awareness, each question would reset the conversation.
Short-Term Memory in AI Systems
Most AI agents maintain short-term memory within a session. That memory helps the system:
- Understand follow-up questions
- Avoid repeating information
- Maintain coherent dialogue
However, when conversations become long or complex, context limits may reduce accuracy.
Research from institutions like Stanford’s Human-Centered AI Institute explains how language models manage context through probability patterns rather than true memory:
https://hai.stanford.edu
Language Prediction: The Core Mechanism
At the center of how AI Agents Talk and Respond to Users lies prediction.
Large language models generate text one word at a time. Each word depends on the words before it. This prediction process creates fluent sentences.
The AI does not retrieve fixed answers from a database. Instead, the system builds responses dynamically.
Why Responses Feel Human
Responses often feel natural because the model trained on large amounts of human writing. That exposure helps the system mimic conversational rhythm, tone shifts, and everyday phrasing.
Still, the model predicts probabilities. It does not reason with awareness.
When AI Agents Use External Tools
Some AI agents go beyond text generation. They connect to external systems when needed.
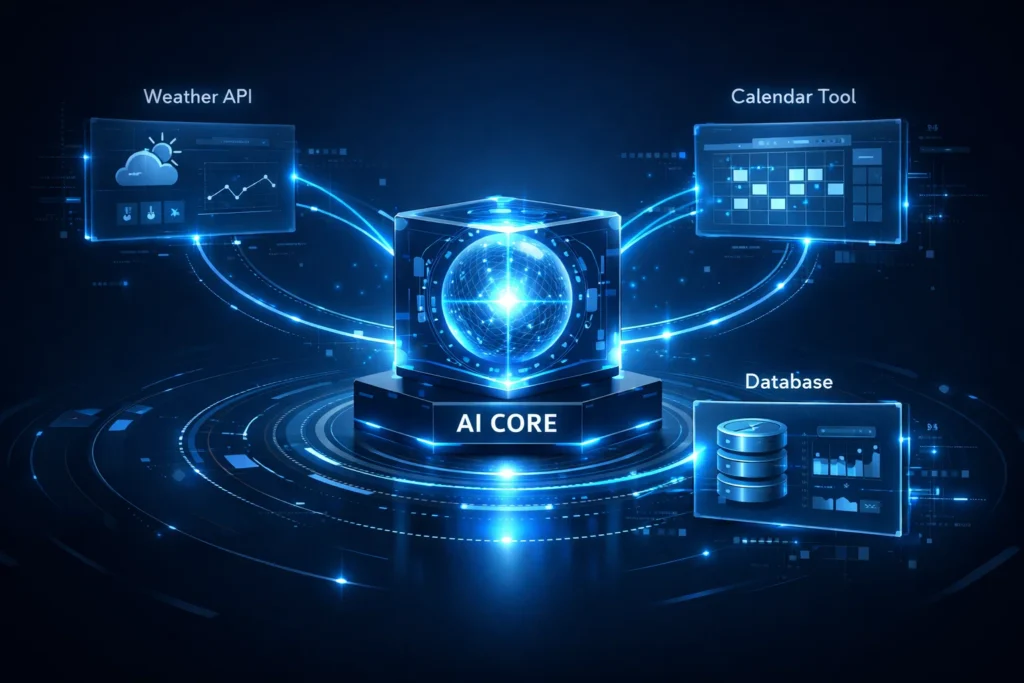
For example, if someone asks for live weather data, the AI may call a weather API. If someone requests calendar scheduling, the system may connect to a calendar service.
The Tool Execution Flow
When tools are involved, the process usually follows this path:
- Identify the need for external data
- Select the appropriate tool
- Execute the request
- Convert results into readable language
This extra layer makes AI agents more capable than basic chatbots.
Handling Ambiguity in Human Language
Human language often lacks precision.
If someone writes, “Book a meeting with Sarah next week,” the AI may respond with a clarification question. The system might ask for the specific day or time.
That clarification happens because the AI detects incomplete instructions.
Rather than guessing incorrectly, well-designed AI agents seek additional details. This behavior improves reliability.
Tone Matching and Response Style
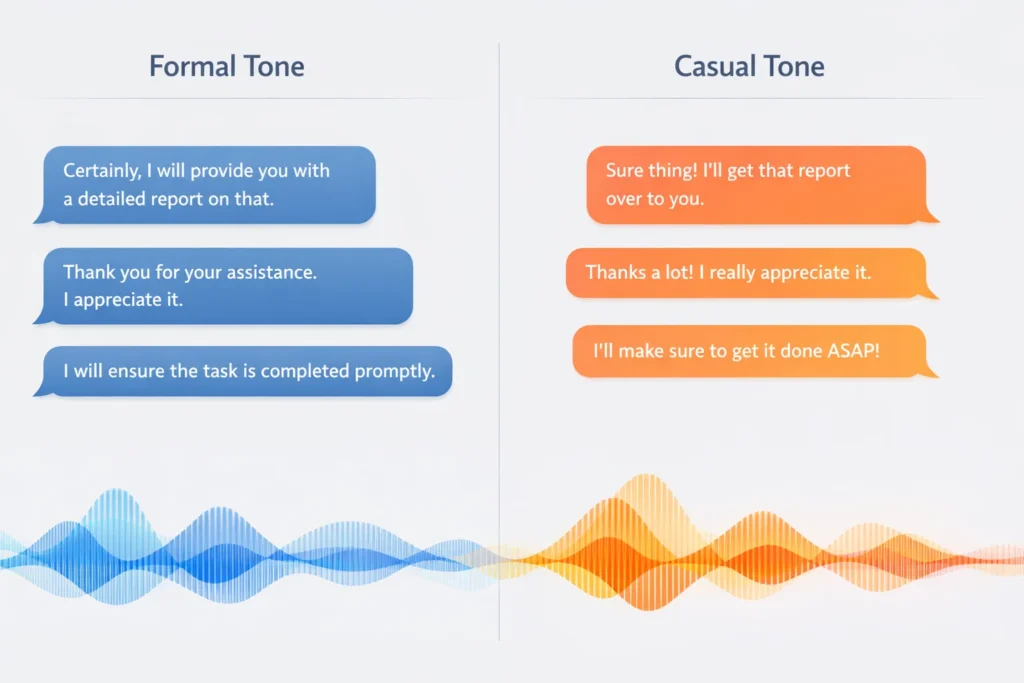
Tone adjustment plays a large role in how AI Agents Talk and Respond to Users.
If someone writes casually, the AI often mirrors that style. If someone writes in a formal tone, the system shifts accordingly.
What Influences Tone?
Several factors shape tone:
- Word choice
- Sentence length
- Emotional cues
- Context of the request
These adjustments make conversations feel more natural and less mechanical.
Why AI Responses Sometimes Fail
Even advanced systems produce errors.
Sometimes instructions are vague. Sometimes context conflicts. Other times, the model generates plausible but incorrect information because prediction favors likelihood over verification.
Understanding this limitation helps users frame better prompts.
Clear and structured requests improve response quality significantly.
Closing Thoughts
Now you have a clearer view of how AI Agents Talk and Respond to Users.
The process relies on intent detection, context tracking, language prediction, and sometimes tool integration. When these layers work together, conversations feel smooth and helpful.
When confusion appears, clearer input often fixes the issue.
AI agents perform best when users communicate clearly.
FAQs
Do AI agents understand meaning like humans?
No. AI agents recognize patterns in language. They do not possess awareness or personal understanding.
How do AI agents remember earlier messages?
Most systems maintain short-term context within a conversation. Some platforms store longer histories depending on design.
Why do AI responses sometimes sound confident but wrong?
Language models predict likely answers. High probability does not always equal factual accuracy.
Can AI agents access real-time information?
Some systems can connect to external tools or APIs. Others rely only on training data.



